Enter sponge cities, an innovative approach to urban design that aims to tackle flooding, manage water resources, and create greener, more resilient environments. But what exactly are sponge cities, and why are they gaining so much attention? Let’s dive in and explore this fascinating concept!
What Are Sponge Cities?
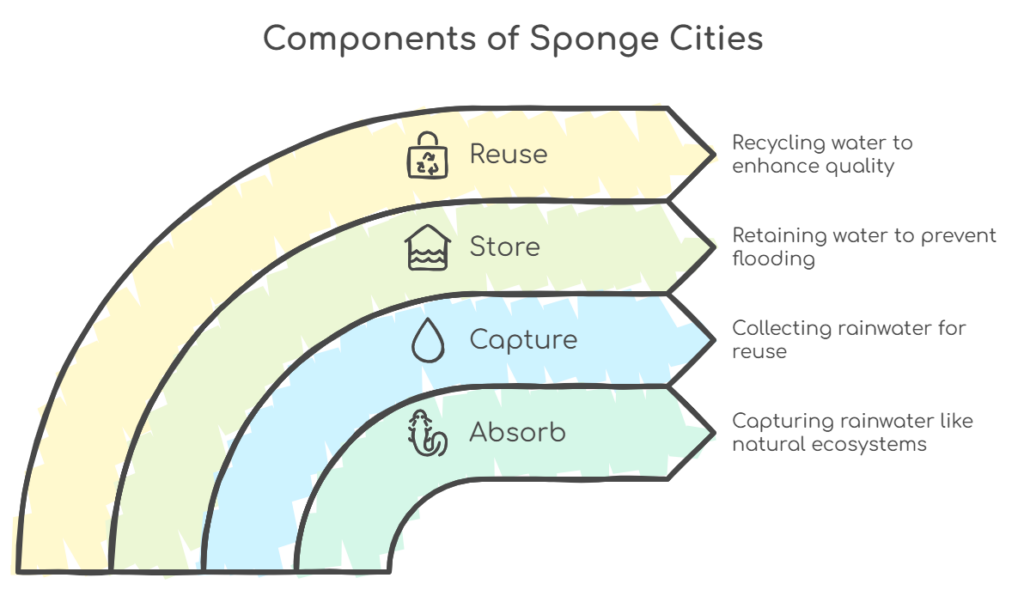
Sponge cities are urban areas designed to absorb, capture, store, and reuse rainwater. Unlike conventional cities where rainwater quickly runs off into drains and rivers, sponge cities mimic natural ecosystems to manage water more sustainably. This approach not only helps prevent flooding but also enhances water quality, supports biodiversity, and improves the overall urban environment.
The Problem: Urban Flooding and Water Management
With climate change bringing more intense and unpredictable rainfall, many cities are grappling with severe flooding. Traditional infrastructure like concrete pavements and storm drains often can’t keep up, leading to waterlogging, property damage, and even loss of life. Moreover, poor water management contributes to water scarcity during dry periods, creating a vicious cycle of excess and deficit.
How Sponge Cities Work
So, how do sponge cities tackle these challenges? Here are some key features and strategies:
1. Green Roofs and Walls
Green roofs and walls are covered with vegetation that absorbs rainwater, reducing runoff and providing insulation. They also improve air quality and add aesthetic value to urban spaces.
2. Permeable Pavements
Unlike traditional pavements, permeable materials allow water to seep through, replenishing groundwater and decreasing surface runoff. This helps mitigate flooding and supports natural water cycles.
3. Rain Gardens and Bioretention Basins
These landscaped areas are designed to capture and filter rainwater. They use plants and soil to remove pollutants, enhancing water quality before it enters the drainage system.
4. Urban Wetlands and Ponds
Creating wetlands and ponds within cities provides natural water storage and filtration. These areas serve as habitats for wildlife and recreational spaces for residents.
5. Smart Water Management Systems
Advanced technologies like sensors and data analytics optimise water distribution and storage, ensuring efficient use and timely responses to flooding events.
Benefits of Sponge Cities
Implementing sponge city principles offers a multitude of benefits:
1. Flood Control
By absorbing and managing rainwater, sponge cities significantly reduce the risk of urban flooding, protecting homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
2. Water Reuse
Captured rainwater can be reused for irrigation, industrial processes, and even potable water, promoting sustainable water use.
3. Enhanced Biodiversity
Green spaces and wetlands create habitats for various species, boosting urban biodiversity and ecosystem health.
4. Improved Air Quality and Urban Cooling
Vegetation in sponge cities helps filter pollutants and provides shade, reducing the urban heat island effect and improving air quality.
5. Community Wellbeing
Green and water-integrated spaces offer recreational opportunities, enhancing the quality of life for city dwellers.
Real-World Examples of Sponge Cities
1. Guangzhou, China
One of the pioneers in sponge city initiatives, Guangzhou has implemented extensive green infrastructure, including permeable pavements, rain gardens, and urban wetlands. These measures have drastically reduced flooding and improved water management.
2. Portland, USA
Portland’s approach focuses on green stormwater infrastructure, such as bioswales and green roofs, to manage rainwater sustainably. The city aims to become a model for resilient urban water management.
3. Rotterdam, Netherlands
Known for its innovative water management, Rotterdam integrates sponge city concepts with its famous floating architecture, creating a harmonious balance between urban development and water resilience.
Challenges and Considerations
While sponge cities offer numerous benefits, there are challenges to overcome:
1. Implementation Costs
Initial investment in green infrastructure can be high, requiring careful planning and financial strategies to ensure feasibility.
2. Maintenance and Upkeep
Green systems require regular maintenance to function effectively, necessitating ongoing commitment from city authorities and communities.
3. Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Adapting sponge city principles to established urban areas can be complex, requiring innovative solutions and collaboration across various sectors.
The Future of Sponge Cities
As cities continue to grow and climate change intensifies, the adoption of sponge city concepts is likely to increase. Future trends include:
1. Enhanced Technological Integration
Smart technologies will play a crucial role in optimising water management, making sponge cities even more efficient and responsive.
2. Policy and Governance Support
Strong policies and supportive governance frameworks are essential to drive the widespread implementation of sponge city initiatives.
3. Community Involvement
Engaging communities in planning and maintaining green infrastructure fosters a sense of ownership and ensures the sustainability of sponge cities.
How You Can Support Sponge Cities
Even if you’re not a city planner, you can contribute to the sponge city movement:
1. Advocate for Green Infrastructure
Support local initiatives that promote green roofs, rain gardens, and permeable pavements in your community.
2. Practice Sustainable Water Use
Conserve water and manage runoff on your property by using rain barrels, planting native vegetation, and reducing impermeable surfaces.
3. Educate Yourself and Others
Learn more about sponge cities and share the knowledge with friends, family, and colleagues to raise awareness and drive collective action.
Conclusion
Sponge cities represent a forward-thinking approach to urban planning, addressing the pressing issues of flooding, water scarcity, and environmental degradation. By embracing green infrastructure and innovative water management strategies, cities can become more resilient, sustainable, and livable. Whether you’re a city official, a resident, or just someone passionate about sustainability, supporting sponge city initiatives is a step towards a better future for all.


